Full Stack Web Development Internship Program
- 29k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
In this Software Testing interview questions article, I have collected the most frequently asked questions by interviewers. These questions are collected after consulting with top industry experts in the field of Manual and Automation testing. If you want to brush up with the software testing basics, which I recommend you to do before going ahead with this Software Testing Interview Questions, take a look at this article on Software Testing Tutorial.
In case you came across some other questions during your interviews or have queries that might be helpful for others as well, do share them in the comment section of this article. Meanwhile, you can maximize the Automation testing career opportunities that are sure to come your way by taking Selenium Online Training with Edureka.
If you are a tech-savvy who wants to up-skill yourself with all the latest technologies, take a look at this list of Top Trending Technologies.
This Edureka video on Top 50 Software Testing Interview Question and Answers will help you to prepare yourself for Software Testing Interviews. It covers questions for beginners, intermediate and experienced professionals.
This Software Testing Interview question is divided into the following parts:
Let’s begin this software testing interview questions with beginners level questions first.
Basically, software testing is a process conducted to view the functionality, performance, and quality of a software application. To do so, run the software under controlled conditions, either trigger or expose defects/bugs hidden in the software, and ensure that all its components conform to predefined requirements. Testing verifies the following: whether the software behaves as expected, performs with Btn effectiveness, and is reliable to the end-users.
Tests can be done at different levels to ensure that the software application is of high quality and working on par. Here are few different kinds of software testing along with a brief description of each:
A test coverage tool is a utility that monitors and quantifies the amount of code under test by a software program. Extra code is run to keep tabs on which lines or branches of code are executed. This gives insight into how far their tests exercise the code and points out whether some functionality of the software might not be fit enough for release to production.
Among the different types of test coverage techniques are:
Black-box testing is testing that is focused on the logic behind a software application’s functionality. It is based on the requirement specifications, which identify how the inputs are handled and translated into outputs.
White-box Testing: It is knowledge of the internal logic, structure, and code of the software to be tested to ensure all possible line/ branch executions have been exercised.
Gray-box testing: This is a kind of mixture, which incorporates both black- and white-box testing ways mentioned herein. The testers know the inner mechanisms only partially, but such knowledge can help them in the setting-up of more complete test cases, which are usually oriented toward integration and system behavior.
The different phases involved in the software testing life cycle are:
| Requirement Analysis | Here, the QA team understands the requirements and identify the testable requirements. |
| Requirement Analysis | Here, the QA team understands the requirements and identify the testable requirements. |
| Test Planning | In this phase, the test strategy is defined. |
| Test Case Development | Here, detailed test cases are defined and developed. |
| Environment Setup | It is a setup of software and hardware for the testing teams to execute test cases. |
| Test Execution | It is the process of executing the code and comparing the expected and actual results. |
| Test Cycle Closure | It involves calling out the testing team member meeting & evaluating cycle completion criteria based on test coverage, quality, cost, time, critical business objectives, and software. |
There are three methods of software testing and they are as follows:
There are mainly four testing levels and they are:
Basically, it starts with the Unit Testing phase and ends with Acceptance Testing.
Software testing is governed by seven principles:
A defect life cycle is a process in which a defect goes through various phases during its entire lifetime. It starts when a defect is found and ends when a defect is closed, after ensuring it’s not reproduced.
Bug or defect life cycle includes the steps as illustrated in the below figure. If you wish to learn in depth about Bug Life Cycle then you can refer my article on Software Testing Tutorial.
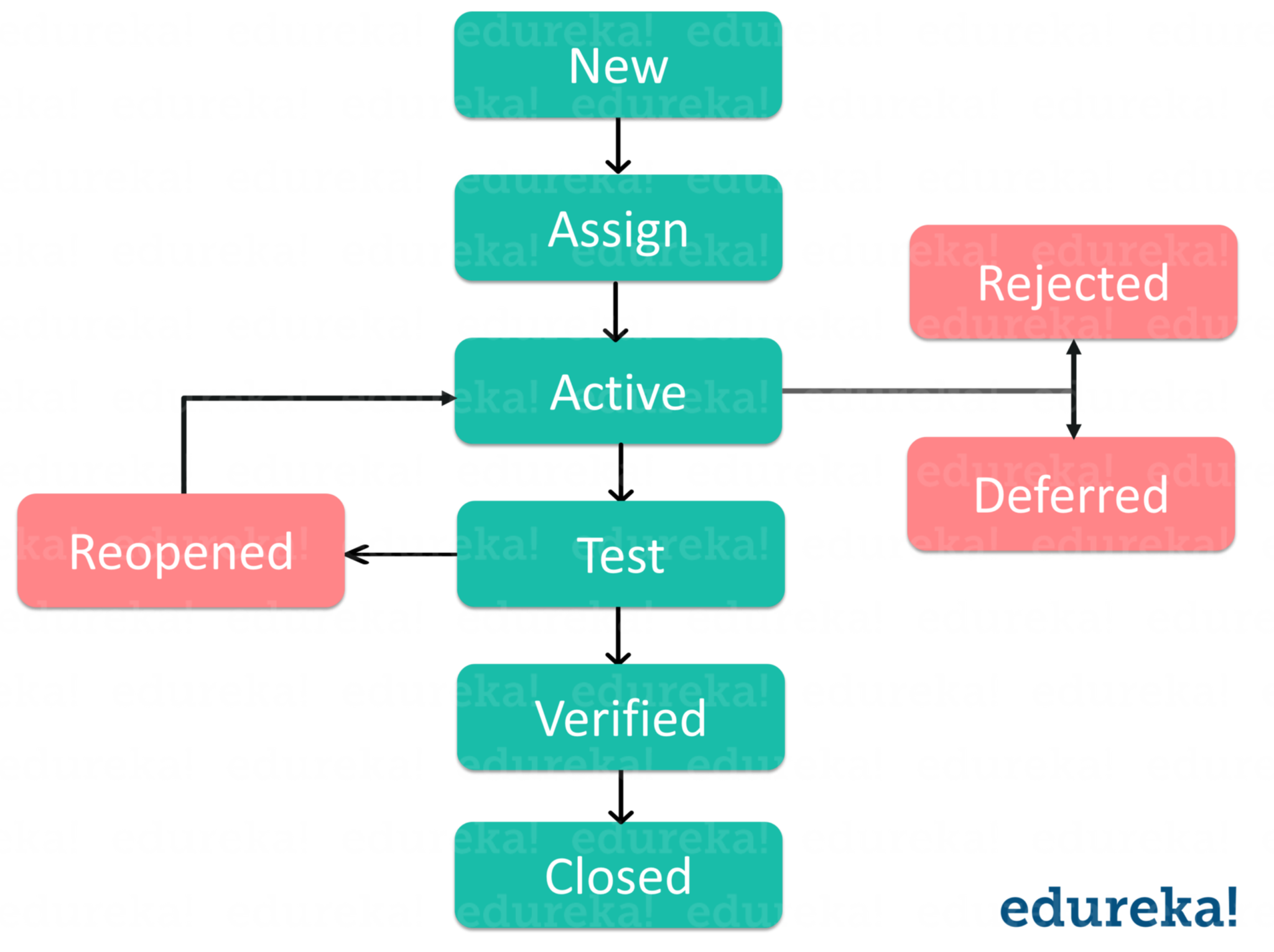 It can vary from organization to organization and also from project to project based on several factors like organization policy, software development model used (like Agile, Iterative), project timelines, team structure etc.
It can vary from organization to organization and also from project to project based on several factors like organization policy, software development model used (like Agile, Iterative), project timelines, team structure etc.
A test case is nothing but a set of conditions or variables under which a tester will determine whether a system under test satisfies requirements or works correctly.
| Functional Testing | Non Functional Testing |
Performed before non-functional testing | Performed after functional testing |
Based on customers expectations | |
Describes what the product does | Describes how the product works |
Verification: It is a static analysis technique. Here, testing is done without executing the code. Examples include – Reviews, Inspection, and walkthrough.
Validation: It is a dynamic analysis technique where testing is done by executing the code. Examples include functional and non-functional testing techniques.
In the V model, the development and QA activities are done simultaneously. There is no discrete phase called Testing, rather testing starts right from the requirement phase. The verification and validation activities go hand in hand.
14. What is exploratory testing?
Exploratory testing means testers explore a computer program like an adventurer. They don’t follow a strict plan but try different things, like a curious detective looking for problems. This helps find mistakes that regular testing might miss, especially in tricky or new parts of the program. Testers take notes while they explore to remember what they did and what they found. It’s like exploring a new place without a map to find interesting things you wouldn’t expect! It also provides a high-level overview of the system that helps evaluate and quickly learn the software.
End to End testing is the process of testing a software system from start to finish. The tester tests the software just like an end-user would. For example, to test a desktop software, the tester would install the software as the user would, open it, use the application as intended, and verify the behavior. Same for a web application.
There is an important difference between end-to-end testing vs. other forms of testing that are more isolated, such as unit testing. In end-to-end testing, the software is tested along with all its dependencies and integrations, such as databases, networks, file systems, and other external services.
16. What is unit testing?
Unit testing is the process of testing a single unit of code in an isolated manner. The unit of code can be a method, a class, or a module. Unit testing aims to focus on the smallest building blocks of code to get confidence to combine them later to produce fully functioning software.
A unit test invokes the code and verifies the result with the expected result. If the expected and actual outcomes match, then the unit test passes. Otherwise, it fails.
17. What is an API?
API stands for Application Programming Interface. It is a means of communication between two software components. An API abstracts the internal workings and complexity of a software program and allows the user of that API to solely focus on the inputs and outputs required to use it.
18. What is a test environment?
A test environment consists of a server/computer on which a tester runs their tests. It is different from a development machine and tries to represent the actual hardware on which the software will run; once it’s in production.
Whenever a new build of the software is released, the tester updates the test environment with the latest build and runs the regression tests suite. Once it passes, the tester moves on to testing new functionality.
19. Explain test scenarios, test scripts, and test cases in software testing.
20. What is a bug in software testing?
A bug in software testing is like a mistake in a computer program. It’s something that the program does that it’s not supposed to do, or it doesn’t do something that it should do. Just like a spelling mistake in a book, bugs can cause the program to act weird or not work correctly. Testers find these bugs so that the programmers can fix them and make the program better.
21. State the difference between bugs and errors
Bugs and errors differ in the following ways:
| Bugs | Erors |
| A bug is a problem in a computer program that causes it to behave in an unintended way. | An error is a mistake made by a human, such as a programmer, while writing the code. |
| It’s a flaw or a mistake in the code that leads to incorrect behavior, unexpected results, or crashes. | It’s the root cause of a bug. If a programmer makes a mistake when writing code, it can lead to a bug in the software. |
| Bugs can be the result of coding mistakes, logic errors, or design flaws. | Errors can include syntax mistakes, logic errors, incorrect calculations, and more. |
A test plan is basically a dynamic document monitored and controlled by the testing manager. The success of a testing project totally depends upon a well-written test plan document that describes software testing scope and activities. It basically serves as a blueprint that outlines the what, when, how, and more of the entire test process
Test report is basically a document that includes a total summary of testing objectives, activities, and results. It is very much required to reflect testing results and gives an opportunity to estimate testing results quickly. It helps us to decide whether the product is ready for release or not. It also helps us determine the current status of the project and the quality of the product. A test report must include the following details:
Test deliverables, also known as test artifacts, are basically a list of all of the documents, tools, and other components that are given to the stakeholders of a software project during the SDLC. Test deliverables are maintained and developed in support of the test. At every phase of SDLC, there are different deliverables as given below:
Before Testing Phase
● Test plans document.
● Test cases documents
● Test Design specifications.
During Testing Phase
● Test Scripts
● Simulators.
● Test Data
● Test Traceability Matrix
● Error logs and execution logs
After testing Phase
● Test Results/reports
● Defect Report
● Installation/ Test procedures guidelines
● Release notes
Different categories of debugging include:
● Brute force debugging
● Backtracking
● Cause elimination
● Program slicing
● Fault tree analysis
Some common mistakes include:
● Poor Scheduling
● Underestimating
● Ignoring small issues
● Not following the exact process
● Improper resource allocation
A user story describes the user’s motivations and what they are trying to accomplish by using the software. Finally, it shows how the user uses the application. It ignores the design and implementation details. A user story aims to focus on the value provided to the end-user instead of the exact inputs they might enter and the expected output.
1. Selenium: a web browser automation tool that automates the test suites you need to run on a web browser.
2. Protractor: An end-to-end test framework for Angular and AngularJS applications. Protractor runs tests against your application running in a real browser, interacting with it as a user would.
3. Cypress: A modern front-end testing tool built for the modern web. Though it’s similar to Selenium and Protractor, it’s architecturally different from them.
4. Jasmine: This is an open-source JavaScript testing framework that allows you to write behaviour-driven tests.
5. JUnit and NUnit: These are unit testing frameworks for Java and C# programming languages, respectively.
It is a testing methodology where the end customer is asked to use the software to see if the product is easy to use, to see the customer’s perception and task time. An accurate way to finalize the customer point of view for usability is by using prototype or mock-up software during the initial stages.
There are three main categories of defects as shown in the below figure:
Basically, the acceptance document is prepared using the following inputs.
The parameter used in software testing to describe the extent to which the source code is tested is known as coverage. There are three basic types of coverage techniques and they are:
Benefits of Automation testing are:
Selenium is an open source tool which is used for automating the tests carried out on web browsers. Since Selenium is open-source, there is no licensing cost involved, which is a major advantage over other testing tools. Other reasons behind Selenium’s ever-growing popularity are:
Related Article: Selenium Interview Questions
Different components of Selenium are:
The locator is nothing but an address that identifies a web element uniquely within the webpage. Thus, to identify web elements accurately and precisely we have different types of locators in Selenium as follows:
XPath also called as XML Path is a language to query XML documents. It is an important strategy to locate elements in selenium. It consists of a path expression along with some conditions. Here, you can easily write XPath script/query to locate any element in the webpage. It is designed to allow the navigation of XML documents, with the purpose of selecting individual elements, attributes, or some other part of an XML document for specific processing. It also produces reliable locators.
It is the direct way to find the element, but the disadvantage of the absolute XPath is that, if there are any changes made in the path of the element then that XPath gets failed. For example: /html/body/div[1]/section/div[1]/div
For Relative XPath, the path starts from the middle of the HTML DOM structure. It begins with the double forward slash (//), which means it can search the element anywhere at the webpage. For example: //input[@id=‘ap_email’]
Exceptions in Selenium are similar to exceptions in other programming languages. The most common exceptions in Selenium are:
Selenium Grid can be used to execute same or different test scripts on multiple platforms and browsers concurrently so as to achieve distributed test execution, testing under different environments and saving execution time remarkably.
The following syntax can be used to launch the Browser:
WebDriver driver = new FirefoxDriver();
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
WebDriver driver = new InternetExplorerDriver();
Testing metrics provide a high-level overview to the management or the developers on how the project is going and the next action steps.

Here are some of the metrics derived from a record of the tests and failures:
● Total number of defects found, ordered by their severity
● Total number of bugs fixed
● Total number of problems caused by an error in the source code vs. configuration or external environmental factors
● Bug find and fix rate over time
● Bugs by produce/feature area
● The average time is taken by a bug since it’s found and fixed.
● Total time spent on new feature development vs. time spent on resolving bugs and failures
● Number of outstanding bugs before a release
● Bugs/failures reported by the customers vs. those found by the testers
43. What is A/B testing?
A/B testing is the process of testing two or more different versions of your software with users to assess which performs better. It is a low-risk way of testing variations of a new or existing functionality.
You can choose a part of your users to use feature A. The other group uses feature B. Then user feedback and response are evaluated using statistical testing to decide the final version of the feature.

Typically, A/B testing is used to test the user experience of different interfaces. This allows the team to quickly gather feedback and test their initial hypothesis.
44. Can you explain sanity testing in software testing?
The term ‘sanity testing’ refers to a subset of regression testing. The sanity testing ensures that the changes made to the code do not adversely affect the system’s performance. After the software build is received, a sanity test is conducted to ensure that the changes made to the code are working correctly. As a checkpoint, this testing is used to determine whether the build can proceed with further testing. Sanity testing focuses on validating the functionality of the application rather than detailed testing.
Features
45. What do you mean by latent defect and masked defect?
Testing is always done after the build and execution phases Earlier we catch a defect, the more cost effective it is. For example, fixing a defect in maintenance is ten times more costly than fixing it during execution.
As test phases start moving ahead environment reality becomes more important. For example, while unit testing, you need the environment to be partly real, but at the acceptance phase you should have a 100% real environment, or we can say it should be the actual real environment.
 The above graph shows during acceptance testing it should be 100% real.
The above graph shows during acceptance testing it should be 100% real.
The following steps can assist in resolving issues during testing:
● Record: Keep track of any problems that arise and resolve them.
● Report: Inform higher-level managers of the issues.
● Control: Establish a process for managing issues.
49. What is defects in software testing?
The term defect refers to a system error that prevents the intended action from being accomplished. Testing is most important when it comes to finding defects. Testing needs to begin early in the development process since defects can be found throughout. As shown in the following figure, defects are divided into three main categories:
50. What is spice in software testing?
SPICE stands for Software Process Improvement and Capability Determination. In the field of software development processes, SPICE is a standard framework for assessing the efficiency and effectiveness of the development process. IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) and ISO (International Organization for Standardization) jointly developed SPICE.
If at the initial stage a defect is identified, then it should be removed during that stage/phase itself rather than at some later stage. It’s a fact that if a defect is delayed for later phases it becomes more costly. The following figure shows how a defect is costly as the phases move forward.
 If a defect is identified and removed during the design phase, it is the most cost effective but when removed during maintenance it becomes twenty times costlier.
If a defect is identified and removed during the design phase, it is the most cost effective but when removed during maintenance it becomes twenty times costlier.
Regression Testing: It is defined as a type of software testing to confirm that a recent code change has not adversely affected existing features.
Confirmation Testing: When a test fails because of the defect, the defect is reported. Then a new version of the software is submitted whose defect is fixed. This is called as confirmation testing or re-testing.
Boundary Value Analysis (BVA) is a black box test design technique which is applied to see if there are any bugs at the boundary of the input domain.
Developers make poor testers. Here are some reasons why:
● They try to test the code to make sure that it works, rather than testing all the ways in which it doesn’t work.
● Since they wrote it themselves, developers tend to be very optimistic about the software and don’t have the correct attitude needed for testing: to break software.
● Developers skip the more sophisticated tests that an experienced tester would perform to break the software. They follow the happy path to execute the code from start to finish with proper inputs, often not enough to get the confidence to ship software in production.
However, it doesn’t mean that developers shouldn’t test the software before sending it to the tester. Developer testing helps find many bugs that are caused by programming errors. These are hard to find for a tester because they don’t always have access to the source code.
It is impossible to exhaustively test software or prove the absence of errors, no matter how specific your test strategy is.
An extensive test that finds hundreds of errors doesn’t imply that it has discovered them all. There could be many more errors that the test might have missed. The absence of errors doesn’t mean there are no errors, and the software is perfect. It could easily mean ineffective or incomplete tests. To prove that a program works, you’d have to test all possible inputs and their combinations.
Consider a simple program that takes a string as an input that is ten characters long. To test it with each possible input, you’d have to enter 2610 names, which is impossible. Since exhaustive testing is not practical, your best strategy as a tester is to pick the test cases that are most likely to find errors. Testing is sufficient when you have enough confidence to release the software and assume it will work as expected.
Any software tester’s goal is to find out as many bugs and problems in the system so that the customers don’t have to. Hence, a good software tester should have a keen eye for detail. They should know the ins and outs of the software they are testing and push every aspect of the software to its limits, to identify bugs that are hard to find with the software’s regular use.
Having the domain knowledge of the application is essential. If a tester doesn’t understand the specific problems the software is trying to solve, they won’t be able to test it thoroughly.
A good tester should keep the end-user in mind when they are testing. Having empathy with the end-user helps the tester ensure that the software is accessible and usable. Simultaneously, the tester should possess basic programming skills to think from a developer’s perspective, which allows them to notice common programming errors such as null-references, out-of-memory errors, etc.
Communication, both written and verbal, is an essential skill for a tester. A tester will frequently have to interact with both the developers and the management. They should be able to explain the bugs and problems found during testing to the developers. For each bug found, a good tester should provide a detailed bug report consisting of all the information a developer would need to fix that problem. They should be able to make a good case to the management if they are uncomfortable releasing the software if it contains unresolved issues.
Usually, in Random testing, data is generated randomly often using a tool. For example, the following figure shows how randomly-generated data is sent to the system.
 This data is generated either using a tool or some automated mechanism. With this randomly generated input, the system is then tested and results are observed accordingly.
This data is generated either using a tool or some automated mechanism. With this randomly generated input, the system is then tested and results are observed accordingly.
To estimate your project, you have to consider the following points:
Usually, black box test cases are written first and white box test cases later. To write black box test cases we need the requirement document and, design or project plan. These documents are easily available at the initial start of the project. White box test cases cannot be started in the initial phase of the project because they need more architecture clarity which is not available at the start of the project. So normally white box test cases are written after black box test cases are written.
The basic components of defect report format include:
Automation testing is very useful in agile methodology and helps in achieving maximum test coverage in a lesser time of the sprint.
By following criteria, the success of Automation testing can be mapped:
To access a website, a user sends a “request” to that website’s server, and the server sends back a response in the form of the website you want to access. To load test a website, quality assurance engineers and automation engineers just need to multiply the number of responses sent to simulate different traffic loads. The web server’s response to the influx of virtual users can then be measured. This is used to determine performance issues and server capacity.
| Selenium | Sikuli |
| It cannot automate flash objects like video player, audio player etc. | It provides extensive support to automate flash objects |
| It has got complicated API | It has a simple API |
| It can automate only web applications | It can automate the web as well as a windows application. |
driver.findElement(By.linkText(“Google”)).click();
This command finds the element using link text and then click on that element. Thus, the user would be re-directed to the corresponding page.
It is an advanced framework which is designed in a way to leverage the benefits by both the developers and testers. It also has an inbuilt exception handling mechanism which lets the program to run without terminating unexpectedly.
Below code helps you to understand how to set test case priority in TestNG.
package TestNG;
import org.testng.annotations.*;
public class SettingPriority {
@Test(priority=0)
public void method1() {
}
@Test(priority=1)
public void method2() {
}
@Test(priority=2)
public void method3() {
}
}
Test Execution Sequence:
Method1 Method2 Method3
| Selenium | Quick Test Professional |
| Selenium supports almost all the popular browsers like Firefox, Chrome, Safari, Internet Explorer, Opera etc | QTP supports Internet Explorer, Firefox and Chrome. QTP only supports Windows Operating System |
| Selenium is distributed as an open source tool and is freely available | QTP is distributed as a licensed tool and is commercialized |
| Selenium supports testing of only web-based applications | QTP supports testing of both the web-based application and windows based application |
Object Repository refers to the collection of web elements belonging to Application Under Test (AUT) along with their locator values. With respect to Selenium, objects can be stored in an excel sheet which can be populated inside the script whenever required.
By using sendKeys()method we can input the text in the text box using Selenium WebDriver.
This section help you practice with the advanced level and scenario based interview questions
Test-Driven-Development (TDD) is a popular software development technique, first introduced by Kent Beck in his book with the same name, published in 1999.
In TDD, a developer working on a feature first writes a failing test, then writes just enough code to make that test pass. Once they have a passing test, they add another failing test and then write just enough code to pass the failing test. This cycle repeats until the developer has the fully working feature. If the code under the test has external dependencies such as database, files, or network, you can mock them to isolate the code.
Benefits of TDD:
● Writing tests first forces you to think about the feature you are trying to build, helping you produce better code.
● As you always have a working set of tests at hand, a failing test indicates that the problem is with the code you just added, reducing the time spent in debugging.
● Writing tests help the developer to clarify the requirements and specification. It’s challenging to write good tests for a poor set of requirements.
● It’s tough to produce high-quality software unless you can test the software after each new change. You can never be sure that your new code didn’t break the working software. TDD gives you the confidence to add new code, as you already have a test in place.
Related Learning: Manual Testing Interview Questions
All web applications run in browsers such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Internet Explorer, Safari, etc. Though they all work primarily the same in implementing the web standards, there are subtle differences in all of them. When building the software, it’s not always possible for the software developer to meticulously test the feature on multiple browsers, noticing the subtle inconsistencies.
In cross-browser testing, a software tester launches the web application in all the supported browsers and tries to test the same functionality on all of them. They note any unexpected behavior in a browser that doesn’t work as expected or looks different; note the behavior and the browser name and version in the test report. This helps the programmer to fix the behavior in all the browsers where it doesn’t work as intended.
74. What are the different types of severity you can assign to a bug?
Though it varies depending on the size and structure of the software development teams, typically, a bug can be assigned the following types of severities, going from low to high:
Low
Medium
High
75. What is alpha testing?
Before you ship the software to the customers, the internal testing team performs alpha testing. Alpha testing is part of the user acceptance testing. Its goal is to identify bugs before the customers start using the software.
76. What is beta testing?
Once you ship the software to the customers after alpha testing, the software’s actual users perform the beta testing in a real production environment. It is one of the final components of user acceptance testing. Beta testing is helpful to get feedback from real people using your software in real environments.
77. What is meant by browser automation?
It’s a process of automatically testing a web application’s functionality in a browser, where a program launches the browser, navigates to the application, and interacts with the user interface by clicking buttons or links, just like an average user would.
The only difference is that the browser automation can test this very quickly and often, whereas the same test would take a human tester a long time. It’s part of automated testing. Some essential tools for browser testing include Selenium, protractor.js, and cypress.
78. What do you mean by Test Matrix and Traceability Matrix?
Test Matrix: It is referred to as a testing tool that is used to capture actual quality, effort, resources, plan, and time required to capture all the phases of software testing. It only covers the testing phase of the life cycle.
Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM): It is referred to as a document, usually present in the form table, that is used to trace and demonstrate the relationship between the requirements and other artifacts of the project right from start to end. In simple words, it maps between test cases and customer requirements.
79. What is static software testing?
Static testing is a technique in which you test the software without actually executing it. It involves doing code walkthroughs, code reviews, peer-reviews, or using sophisticated tools such as eslint, StyleCop to perform static analysis of the source code. Static testing is typically performed during software development.
In contrast to static testing, dynamic software testing tests the software when it’s executing. The tester runs the software in a test environment and goes through all the steps involved, entering the inputs and verifying the actual output with the expected result.
An end user is the most important person because he is the one who has to use the product and has a keen interest that anyone else in the project.
 Above figure illustrates the input that is essential from the user end.
Above figure illustrates the input that is essential from the user end.
A workbench at its core is a way of documenting how a specific activity has to be performed. It is often referred to as phases, steps, and tasks as shown in the following figure.
 There are five tasks for every workbench and they are as follows:
There are five tasks for every workbench and they are as follows:
Defect cascading is a defect which is caused by another defect. One defect triggers the other defect. When a defect is present in any stage but is not identified, hide to other phases without getting noticed. This will result in an increase in the number of defects.
Let us understand this by an example.
You are designing the Login Module of a WebPage:
In phase 1 – You are designing Register User Module for Login and mobile number is mandatory but you can leave it blank due to a bug that gets unnoticed.
In Phase 2 – You will design the login form having username and password. The password is OTP which will be sent to User’s registered mobile number.
Now as Register module has a bug that mobile number can be left blank so this may lead to Login failure or maybe some system error or crash if a null mobile number is not handled. This is known as defect cascading.
84. What are the different strategies for rollout to end users?
The strategies to be followed for rollout are as follows:
This is a tricky question which the interviewer might present to you. He can provide a situation wherein there are 20 links in a web page, and we have to verify which of those 20 links are working and how many are not working (broken).
As you have to verify the working of every link, the workaround is that you need to send HTTP requests to all of the links on the web page and analyze the response. Whenever you use driver.get() method to navigate to a URL, it will respond with a status of 200 – OK. This indicates that the link is working and it has been obtained. Whereas any other status indicates that the link is broken.
Let’s now understand how to do that.
First, we have to use the anchor tags <a> to determine the different hyperlinks on the web page. For every <a> tag, we can use the attribute ‘href’ value to obtain the hyperlinks and then analyze the response received when used in driver.get() method.
If frame name and frame id is not available, then we can use frame by index. For example, there are 3 frames in a web page and if none of them have a frame name and frame id, then we can still select those frames by using frame (zero-based) index attribute. All the frame will have an index number like the first frame would be at index “0”, the second at index “1” and the third at index “2”.
driver.switchTo().frame(int arg0);
By using the TakeScreenshot function you can take a screenshot. With the help of getScreenshotAs() method, you can simply save that screenshot. Example: File scrFile = ((TakeScreenshot)driver).getScreenshotAs(outputType.FILE);
If there is a pop up for logging in, we need to use the explicit command and verify if the alert is actually present. The below code helps you understand the use of explicit wait command.
WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver, 10); Alert alert = wait.until(ExpectedConditions.alertIsPresent()); alert.authenticateUsing(new UserAndPassword(**username**, **password**));
89. How to skip a method or a code block in TestNG?
To skip a particular test method or a code, then you can set the ‘enabled’ parameter in test annotation to false.
@Test(enabled = false)
WebElement sample = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[contains(text(), 'data')]"));
It defines a variable sample of type WebElement, and uses an XPath search to initialize it with a reference to an element that contains the text value “data”.
This brings us to the end of this article on Top 50 Software Testing Interview Questions. Hope it helped in adding up to your knowledge. Wishing you all the best for your interview. You can also check our blog on QA automation interview questions. Happy learning.
Prepare for a software testing interview by immersing yourself in fundamental concepts of Software Testing and relevant tools, practicing problem-solving through test scenarios, understanding SDLC/STLC processes, domain knowledge if required, resume polishing, practicing behavioral questions, researching the company, asking worthy questions, and mock interviews.
The seven steps of software testing are mentioned below:
SDLC stands for Software Development Life Cycle and is the framework that helps development teams effectively plan, design, develop, test, and deploy software applications for maintenance.
STLC stands for Software Test Life Cycle, and it is a defined process outlining the approach used and activities on testing within SDLC. This allows appropriate testing to be run in finding defects and changing them prior to rolling them out to end-users.
The following are the four kinds of software tests common in reference:
Software testing is a process or act of running or executing software in a normally systematic way to validate the quality of the software at levels such as unit, integration, and system testing, using various techniques that can be referred to as black-box and white-box testing. It is meant to verify functionality and integrity of the code in such an activity, whose objective is to find problems early, reduce cost, and improve the quality of software before release.
If you found this “Software Testing Interview Questions” article relevant, check out the Software Testing Course by Edureka, a trusted online learning company with a network of more than 250,000 satisfied learners spread across the globe.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section on this Software Testing Interview Questions and we will get back to you.
 REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR
REGISTER FOR FREE WEBINAR  Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
edureka.co
